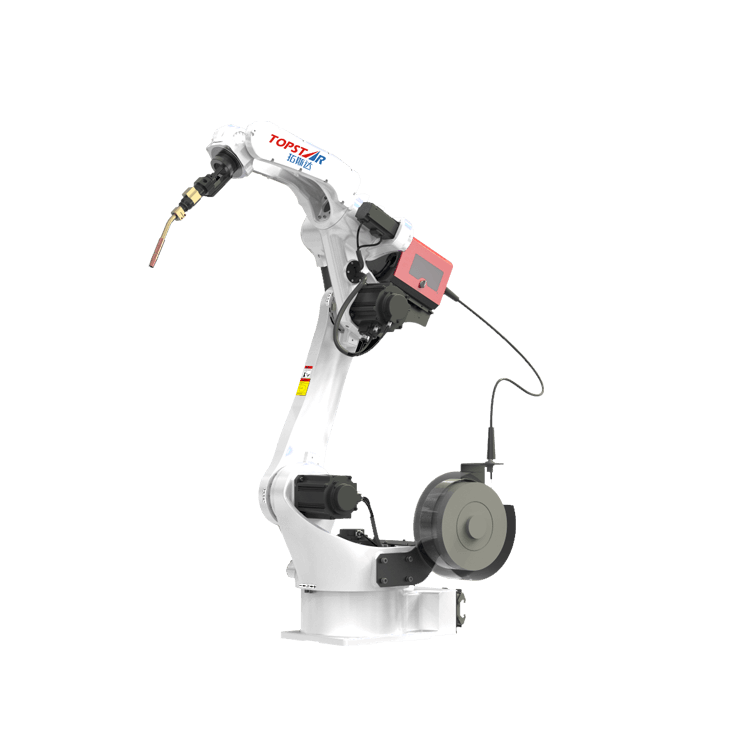
The Six-axis industrial robot is a critical tool for improving the efficiency of manufacturing processes in industrial fields such as precision production and metal machinery. In addition to paying attention to their operating performance, operators cannot ignore their maintenance during daily use. This is a critical process. Combining many years of experience in manufacturing and maintenance, we will provide you with maintenance tips for six-axis industrial robots in this article, which operators can implement to extend their service life.
Regular lubrication of Six-Axis Industrial Robot to ensure smooth movement
Regular lubrication is essential for the optimal performance of six-axis industrial robots, guaranteeing smooth movement and enhancing overall operational efficiency. This maintenance practice involves the application of specific lubricants to the robot’s moving components, including joints, gears, and bearings. By reducing friction, preventing wear, and minimizing heat generation, lubrication contributes to the machine’s longevity and reliable functionality. Common lubricants include oils, greases, and dry lubricants, each chosen based on its suitability for specific applications. The benefits of regular lubrication include minimizing friction-related wear, reducing the risk of component failure, extending the robot’s service life, dissipating heat, and preserving smooth and precise movement, ultimately maintaining the machine’s precision and accuracy.

Perform calibration and accuracy checks on the six-axis industrial robot!
Calibration is a systematic process integral to fine-tuning the control systems, feedback devices, and sensors of six-axis industrial robots to meet established standards. These standards may be industry specifications or project-specific requirements. During calibration, parameters like joint angles, tool position, and end-effector orientation are adjusted to eliminate deviations from desired values.
Accuracy checks follow the calibration process, consistently evaluating a machine’s ability to achieve accurate and repeatable motion. These assessments involve measuring machine components’ position and orientation and comparing them to expected values. High-precision instruments such as laser trackers or coordinate measuring machines are often employed. Calibration and accuracy checks are tailored to the machine’s design, complexity, and application, considering factors like clearance, thermal expansion, and mechanical wear. Advanced techniques, including laser interferometry and kinematic modeling, are applied to highly complex six-axis industrial robots.
Perform inspections of cable and wiring systems
Regular inspections of cable and wiring systems are crucial for maintaining the reliability and safety of six-axis industrial robots. These inspections involve a comprehensive examination of electrical components, cables, and wire harnesses to identify potential issues that could impact the robot’s performance or pose safety risks.
Cables and wiring systems are vital in transmitting power, signals, and control commands between different robot parts. Inspectors conduct visual inspections to check for signs of wear, cuts, or exposed wires, with particular attention to areas experiencing repetitive motion. Additionally, operators perform electrical testing, including continuity testing, insulation resistance measurements, and signal integrity checks. These tests ensure safe electrical connections and reliable signal transmission, contributing to the overall reliability and safety of the six-axis industrial robot.

Perform software updates and system diagnostics
Software updates for six-axis industrial robots encompass enhancements to the robot operating system, control algorithms, programming interfaces, and application-specific software. These updates improve accuracy, speed, and efficiency while ensuring compatibility with new peripherals, sensors, or programming languages. Before initiating updates, operators perform a system backup to safeguard existing configurations and programming. This precaution allows for a seamless restoration to the previous state in case unexpected issues arise during the update process.
Operators install the new software version on the robot’s control system, potentially requiring rebooting, recalibrating, or reconfiguring specific parameters. Thorough testing and verification follow the update to confirm the robot’s proper operation and the intactness of safety features. System diagnostics play a vital role in maintaining a six-axis industrial robot. Diagnostics utilize built-in self-tests, remote monitoring systems, and external diagnostic equipment to evaluate hardware components, sensors, actuators, and communication interfaces. Operators leverage these diagnostics to minimize downtime and prevent unforeseen failures.
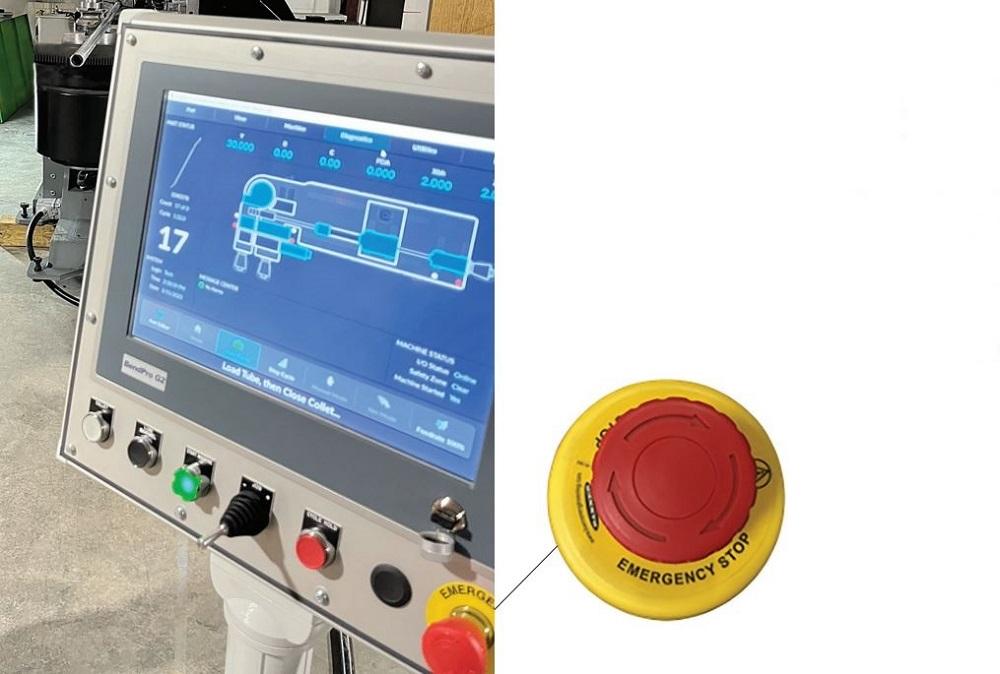
Perform emergency stop system testing
Activation of the emergency stop system is a critical safety feature in six-axis industrial robots, rapidly bringing the robot to a controlled stop to prevent accidents, protect operators, and avoid equipment or workpiece damage.
To conduct an emergency stop system test, operators follow predefined procedures or safety guidelines provided by the manufacturer. This may involve activating an emergency stop button switch or triggering the emergency stop function through a designated control interface. Activation mechanisms vary based on the robot’s design and implemented safety protocols.
Operators observe the robot’s response during the test, ensuring an immediate complete stop with all movements halted and power cut to relevant components. Visual and audible indicators confirm the successful activation of the emergency stop system. Post-test, operators verify that the system has effectively disconnected power and stopped all dangerous movements. A thorough check of the robot’s condition allows for any necessary maintenance or adjustments, enhancing the reliability of the emergency stop system.

Maintain regular maintenance
Proactive and regular maintenance ensures six-axis industrial robots’ longevity, accuracy, and reliability. By adhering to these maintenance practices, operators can streamline the production process, minimize downtime, and ultimately optimize the overall efficiency of the manufacturing process.
TRENDING POSTS
- TOPSTAR Global Open Day 2025: Humanoid Robot Debuts, Pioneering a New Decade of Intelligent Manufacturing 2024/01/12
- Topstar Showcases TE II Electric Injection Molding Machines at InterPlas Thailand 2025 2024/01/12
- Topstar Expands Its Ecosystem Partnerships to Drive Smart Manufacturing Innovation 2024/01/12
- What factors can cause delays in the injection molding process of plastic molding machine? 2024/01/12
HOT TOPIC
- .ervo motor-driven linear robots
- •
- 1.0 guangdong topstar technology co. ltd
- 1.0 topstar china
- 1.0 topstar robot
- 11
- 160℃ mold temperature controller
- 170 ton injection molding machine
- 2
- 21
- 220-ton injection molding machine
- 23
- 260 ton injection molding machine
- 3 axis robot
- 3 axis robots
- 3 in 1 Compact Dehumidifying Dryer
- 3-axis robot
- 3-axis robots
- 39
- 41
- 460T injection molding machine
- 5-axis CNC machine
- 62
- 90 ton injection molding machine
- accuracy
- Air Chillers
- all electric injection molding machine
- all electric injection molding machines
- all-electric injection molding machine
- All-electric injection molding machines
- and overall production quality. Therefore
- AP-RubberPlas
- automated injection molding machine
- Automation changed engineering
- automation of injection molding robots
- automotive parts injection molding
- auxiliary machine
- Bench Injection Molding Machine
- Cabinet dryer manufacturers
- Cabinet dryers
- chiller
- CNC Drilling Machine
- CNC Drilling Machines
- cnc engraving machine manufacturer
- cnc laser cutting machine manufacturer
- CNC machine
- CNC Machine Center
- CNC Machine for Sale
- CNC Machine Manufacturing
- CNC Machine Tool
- CNC machine tool product
- CNC Machining Center
- CNC wood carving machine
- Cooling system
- Cross-Walking Single Axis Servo Cylinder Robot
- Cross-Walking Single-Axis Servo Cylinder Robot
- Cross-Walking Three-Axis/Five-Axis Servo Driven Robot
- cross-walking three-axis/five-axis servo-driven robot
- Dehumidifier Dryer
- Dehumidifying Dryer
- delta parallel robot
- Desktop Injection Molding Machine
- Desktop injection molding machines
- Desktop Molding Machine
- desktop plastic injection machine
- Desktop Plastic Injection Molding Machine
- Digital Transformation
- direct clamp injection molding machine
- Direct clamp injection molding machines
- Dosing & mixing system
- Drilling Centers
- Drying and dehumidification system
- drying and dehumidifying equipment
- Drying and Dehumidifying System
- drying system
- effective and efficient. Cabinet dryers are also used in other industries where large quantities of material need to be dried
- efficient injection molding machine
- elbow hydraulic injection molding machines
- electric injection molding machine
- electric injection molding machines
- energy-efficient injection molding robot
- energy-efficient water chiller
- energy-efficient water chillers
- energy-saving injection molding machine
- etc. Among injection molding robots
- exhibition
- features of CNC machine
- Feeding And Conveying System
- Five Axis Machine Center
- Flexible Production Line
- Fully automatic injection molding machine
- Gathering Topstar
- giant injection molding machine
- GMU-600 5-Axis Machining Center
- Granulating & Recycling System
- granulator machine
- Heavy duty injection molding machine
- High-precision electric molding machines
- high-precision plastic molding machines
- high-speed all electric injection molding machine
- high-speed electric injection molding machine
- High-Speed Packaging Injection Molding
- Honeycomb rotor dehumidifier
- Hopper Dryers
- horizontal injection molding machine
- Horizontal Injection Molding Machines
- Horizontal Injection Moulding Machine
- Horizontal Mixer manufacturer
- How The CNC Machine Works
- hybrid injection molding machine
- hydraulic injection molding machine
- Hydraulic Injection Molding Machines
- in this article
- Industrial AI
- Industrial Automation
- Industrial robot
- Industrial Robot Chinese brand
- industrial robot parts
- industrial robot supplier
- Industrial robots
- Industry Chain
- Injection Manipulator
- injection manipulator robot
- injection mold machines
- Injection molding
- Injection molding automation
- Injection Molding Automation Solution
- injection molding dryer
- Injection molding equipment
- injection molding hopper dryer
- Injection molding machine
- injection molding machine brand
- Injection Molding Machine Factory
- Injection Molding Machine Manufacture
- Injection molding machine manufacturer
- injection molding machine manufacturers
- Injection molding machine procurement
- injection molding machine robotic arm
- injection molding machine with a robot
- Injection molding machines
- injection molding material dehumidifying
- injection molding plant
- injection molding process
- Injection Molding Robot
- injection molding robot arm
- Injection molding robot automation
- Injection molding robotic arm
- injection molding robots
- Injection moulding machine
- injection moulding machines
- Injection Moulding Robots
- Injection Robot
- Injection robot arm
- Injection robot manufacturer
- Injection robot wholesale
- injection robots
- Intelligent Factory
- intelligent injection molding machines
- Intelligent Manufacturing
- intelligent mold temperature
- intelligent mold temperature controller
- Intelligent mould temperature controller
- InterPlas Thailand 2025
- Introducing Injection Robot
- It is the best choice for drying large quantities of material at once. Cabinetmakers use these machines because they are fast
- Large flow water type mold temperature controller
- large injection molding machine
- large injection molding machines
- Learn what industrial automation and robotics is
- linear robot
- linear robots
- low speed sound-proof granulator
- machine plastic molding
- make sure to add some! Improvements (2) Keyphrase in introduction: Your keyphrase or its synonyms appear in the first paragraph of the copy
- manipulator machine
- manufacturing
- Manufacturing Innovation
- medical grade injection molding machines
- Medical Injection Molding
- medical injection molding machine
- medical injection molding machines
- micro injection molding machine
- middle speed granulator
- Mini CNC machine manufacturers.
- mobile cover making machine
- Mold Temperature Control System
- mold temperature controller
- mold temperature controllers
- molding machine
- molding material Dehumidifying System
- mould temperature control system
- mould temperature controller
- mould temperature controllers
- New electric injection molding machine
- nitrogen dryer manufacturer
- nitrogen dryer system manufacturer
- Oil type mold temperature controller
- Oil type mold temperature controllers
- open day
- optical component injection molding
- Outbound links: No outbound links appear in this page. Add some! Images: No images appear on this page. Add some! Internal links: No internal links appear in this page
- packaging injection molding
- Packaging Solutions
- PET Preform injection molding
- phone case maker machine
- phone case making machine
- phone cover making machine
- PID Control Mold Temperature Controller
- plastic bottle making machine
- plastic bottle manufacturing
- plastic bucket making machine
- plastic bucket manufacturing
- Plastic chair making machine
- plastic forming equipment
- plastic hopper dryer
- plastic injection machine
- plastic injection machines
- plastic injection molding
- Plastic injection molding equipment
- Plastic injection molding machine
- Plastic Injection Molding Machines
- plastic injection moulding machine
- plastic injection moulding machines
- plastic injection robot
- plastic molding
- Plastic Molding Industry
- Plastic Molding machine
- plastic molding machine 1
- Plastic Molding Machines
- plastic molding press
- plastic moulding machine
- plastic phone case making machine
- plastic-molding machine
- powerful granulator
- Powerful Type Sound-Proof Granulator
- precision injection molding
- precision injection molding machines
- production of plastic seats
- pure water mould temperature controller
- Robot injection molding
- robot injection molding machine
- robot manufacturing companies
- Robotic arm for injection molding machine
- robotic injection molding machines
- robotics in injection molding
- SCARA robot
- SCARA robots
- Service-oriented manufacturing
- Servo Cylinder Robot
- servo driven robot
- Servo Driven Robots
- servo injection molding machine
- servo injection robots
- servo motor-driven linear robots
- servo-driven 3-axis robot
- Servo-driven injection molding machine
- Servo-Driven Robot
- Setup of injection machine
- Silicone Injection Molding Machine
- six-axis industrial robot
- Smart Manufacturing
- Stainless Hopper Dryer
- Stainless Hopper Dryers
- star club
- swing arm robot
- take-out robot
- take-out robots
- Thailand 4.0
- the choice between servo-driven robots and hydraulic robots will have a certain impact on efficiency
- the most popular injection molding machine
- the type of injection molding robot
- TIC2000 Control System
- TMII injection molding machine
- toggle clamp injection molding machine
- Toggle Hydraulic Injection Molding Machines
- toggle injection molding machine
- Top 10 brands of injection robots
- Topstar
- Topstar Electric Injection Molding Machine InterPlas Thailand 2025 Smart Manufacturing Thailand 4.0
- Topstar Engineering
- Topstar Industrial Robots
- Topstar injection molding intelligent
- Topstar Scara Robots
- Useful Injection molding machine
- Vertical machining centers
- volumetric type blender
- water chiller
- water chillers
- water distributor
- water type mold temperature controller
- Water Type MoldTemperature Controller
- Water-Type Mould Temperature Controllers
- We often face choices when performing injection molding. We will choose the type of injection molding machine
- wholesale of injection molding machines
- x carve CNC
- 热门查询 点击次数 展示 排名 topstar
